The liver plays a vital role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. It performs various essential functions, such as filtering toxins from the blood, producing bile for digestion, storing essential nutrients, and metabolizing drugs. However, the liver is also susceptible to numerous diseases that can severely impact its functionality.
In this comprehensive article, we will explore the ten most common diseases that damage the liver, understand their causes, symptoms, and available treatments. Moreover, we will discuss preventive measures to help maintain a healthy liver.
Table of Contents
- 1 1. Hepatitis C: The Silent Killer
- 2 2. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ARLD)
- 3 3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- 4 4. Hepatitis B: A Global Health Concern
- 5 5. Cirrhosis: The Irreversible Scarring
- 6 6. Autoimmune Hepatitis: When the Body Attacks Itself
- 7 7. Liver Cancer: A Growing Concern
- 8 8. Wilson Disease: A Rare Genetic Disorder
- 9 9. Hemochromatosis: Iron Overload
- 10 10. Gallstones: The Biliary Menace
- 11 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
- 12 Conclusion
1. Hepatitis C: The Silent Killer
Hepatitis C is a viral infection that primarily affects the liver. It is often referred to as the “silent killer” due to its asymptomatic nature in the early stages. This disease spreads through contact with infected blood, such as sharing needles or unscreened blood transfusions. Hepatitis C can lead to chronic liver inflammation, cirrhosis, and even liver cancer if left untreated. Fortunately, advancements in medical science have led to the development of highly effective antiviral medications to cure hepatitis C.
2. Alcohol-Related Liver Disease (ARLD)
Excessive alcohol consumption can have severe consequences for the liver. ARLD encompasses a range of liver conditions, including fatty liver disease, alcoholic hepatitis, and alcoholic cirrhosis. Prolonged alcohol abuse causes inflammation and scarring of the liver, leading to liver dysfunction. The best prevention for ARLD is to limit alcohol consumption and seek help if struggling with alcohol dependency. Early intervention and treatment can prevent further liver damage.
3. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver cells. It is commonly associated with obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome. NAFLD can progress to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), a more severe condition involving liver inflammation and potential scarring. Lifestyle modifications, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management, are crucial for preventing and managing NAFLD.
4. Hepatitis B: A Global Health Concern
Hepatitis B is a viral infection that can cause acute and chronic liver disease. It is transmitted through contact with infected blood or other body fluids, such as unprotected sex or sharing contaminated needles.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 250 million people worldwide are living with chronic hepatitis B infection. Vaccination is the most effective method of preventing hepatitis B. It is essential to complete the full vaccination course for long-term protection.
5. Cirrhosis: The Irreversible Scarring
Cirrhosis is a late-stage liver disease characterized by extensive scarring and loss of liver function. It can result from various causes, including chronic viral hepatitis, excessive alcohol consumption, fatty liver disease, and autoimmune conditions. Cirrhosis is irreversible, but early detection and management can slow down its progression and improve quality of life. Treatment may involve lifestyle changes, medications, and in severe cases, liver transplantation.
6. Autoimmune Hepatitis: When the Body Attacks Itself
Autoimmune hepatitis is a chronic liver disease caused by the immune system mistakenly attacking liver cells. The exact cause of autoimmune hepatitis remains unknown, but genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role. This condition often presents with fatigue, jaundice, abdominal discomfort, and elevated liver enzymes. Treatment involves suppressing the immune response with medications to prevent further liver damage.
7. Liver Cancer: A Growing Concern
Liver cancer, also known as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide. Chronic liver diseases, such as viral hepatitis and cirrhosis, significantly increase the risk of developing liver cancer. Early detection through regular screenings and appropriate treatment can improve outcomes. Treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, or liver transplantation, depending on the stage and severity of the cancer.
8. Wilson Disease: A Rare Genetic Disorder
Wilson disease is a rare genetic disorder that causes copper to accumulate in the liver, brain, and other vital organs. The excess copper damages liver cells and leads to liver dysfunction. Symptoms of Wilson disease can vary, ranging from fatigue and abdominal pain to neurological problems such as tremors and difficulty speaking. Early diagnosis and lifelong treatment with medications to remove excess copper are crucial for managing Wilson disease effectively.
9. Hemochromatosis: Iron Overload
Hemochromatosis is a genetic disorder characterized by excessive absorption of dietary iron. The excess iron accumulates in various organs, including the liver, leading to tissue damage and dysfunction. Symptoms may include fatigue, joint pain, and abdominal discomfort. Treatment involves regular blood removal (phlebotomy) to reduce iron levels and dietary modifications. Early detection and intervention can prevent complications and maintain liver health.
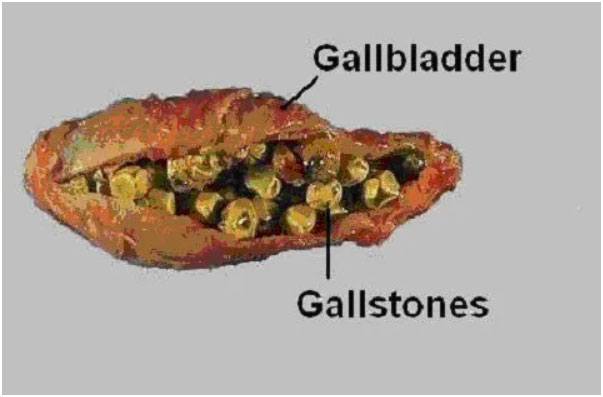
10. Gallstones: The Biliary Menace
Gallstones are hardened deposits that form in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. These stones can obstruct the bile ducts, causing inflammation and potential liver damage.
While gallstones primarily affect the gallbladder, their presence can lead to complications in the liver. Treatment options include medication to dissolve the stones, minimally invasive procedures to remove them, or in severe cases, surgical removal of the gallbladder.
NEXT POST: Kim Kardashian shares adorable photo of baby North posing with five dolls to mark North’s 10th bday
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Can liver diseases be prevented?
Yes, many liver diseases can be prevented through lifestyle modifications and preventive measures. Avoid excessive alcohol consumption, maintain a healthy weight, practice safe sex, and get vaccinated for hepatitis B. Additionally, regular exercise, a balanced diet, and avoiding exposure to toxins can contribute to liver health.
2. How often should I get tested for liver diseases?
The frequency of testing depends on various factors, including your overall health, family history, and lifestyle choices. It is advisable to consult with a healthcare professional who can assess your individual risk factors and recommend an appropriate screening schedule.
3. Are there any natural remedies for liver diseases?
While certain natural remedies may have potential benefits for liver health, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider before trying any alternative treatments. Some herbs, such as milk thistle and turmeric, have shown promise in supporting liver function, but their efficacy and safety vary. It is crucial to prioritize evidence-based medical interventions for the management of liver diseases.
4. Can liver damage be reversed?
In some cases, liver damage can be reversed or halted through timely intervention and lifestyle changes. However, the extent of reversibility depends on the specific condition, the severity of the damage, and individual factors. Seeking medical advice and adhering to recommended treatment plans can optimize the chances of successful management and potential recovery.
5. Is it possible to live a healthy life with liver disease?
Yes, with appropriate medical care, lifestyle modifications, and adherence to treatment plans, it is possible to lead a fulfilling life despite liver disease. Regular monitoring, healthy habits, and emotional support can significantly improve the quality of life for individuals living with liver diseases.
6. Can liver diseases be hereditary?
Some liver diseases have a genetic component and can be inherited from parents. Conditions such as Wilson disease and hemochromatosis are examples of genetic liver disorders. It is important to be aware of your family medical history and inform your healthcare provider to assess any potential genetic risks.
Conclusion
Maintaining a healthy liver is crucial for overall well-being. Understanding the ten most common diseases that damage the liver, their causes, symptoms, and preventive measures empowers individuals to take proactive steps in liver health management. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying informed about the risks, and seeking medical guidance, we can protect our liver and preserve its vital functions.